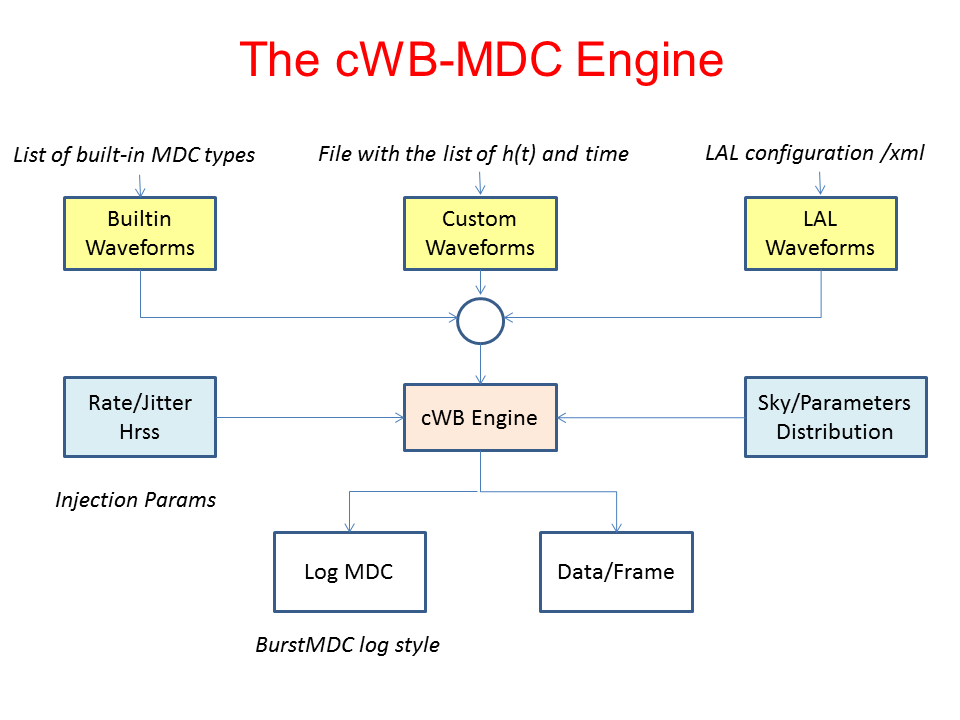
MDC Engine¶
This page provides an overview of the procedure to generate MDC signals for simulation studies with the CWB pipeline.
How to generate MDC signals¶
The generation of MDC signals is based on the following class:
This uses an internal built-in generator for creating simulated Burst-like signals (similar to the BurstMDC) and the LAL library to generate signals modeling coalescing binary systems. For the two classes of signals, different kinds of waveforms can be generated, with different sky distributions.
The following list provides instructions on how to do generate MDC signals. |
Further examples available in the cwb tutorials macros
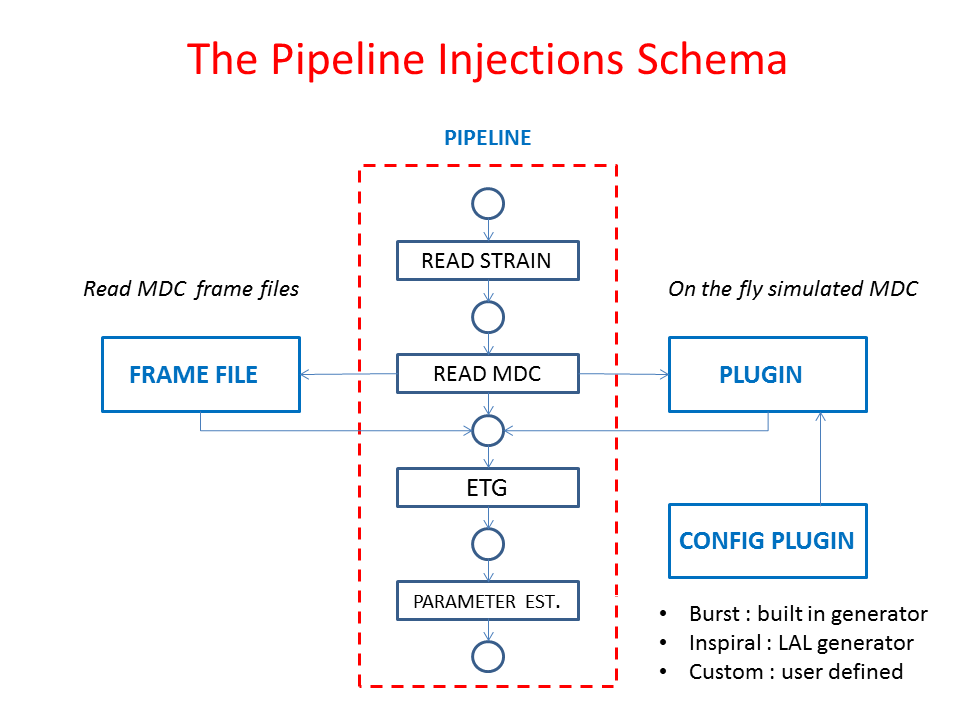
How to inject MDC signals¶
The CWB pipeline can read the MDC simulated signals from frame files or via the ‘on-the-fly’ approach. In particular, the ‘on-the-fly’ approach requires the following plugin: - CWB_Plugin_MDC_OTF.C (see How to use plugins on the configurion of the plugins used for CWB analyses). The generation of MDC simulated signals can be customised by using specific configuration plugins. Examples of configuration plugins for different classes of waveforms are collected in the following list:
- CWB_Plugin_MDC_OTF_Config_BRST.C configuration plugin to generate ‘on the fly’ Burst-like MDC simulated signals
- CWB_Plugin_MDC_OTF_Config_eBBH.C configuration plugin to generate ‘on the fly’ MDC simulated signals from eccentric black hole binaries
- CWB_Plugin_MDC_OTF_Config_NSNS.C configuration plugin to generate ‘on the fly’ MDC simulated signals from neutron star binaries via the LAL libraries. Comment : in this example, the signal is generated by using EOBNRv2 waveforms. For the case of two neutron stars, this waveform provides an accurate description of the signal during the early inspiral stage, whereas is no longer accurate in the late inspiral, merger and ringdown stages due to the mass transfer between the two neutron stars.
- CWB_Plugin_MDC_OTF_Config_EOBNRv2pseudoFourPN.C configuration plugin to generate ‘on the fly’ MDC simulated signals from coalescing binaries with the EOBNRv2 waveforms implemented in the LAL libraries
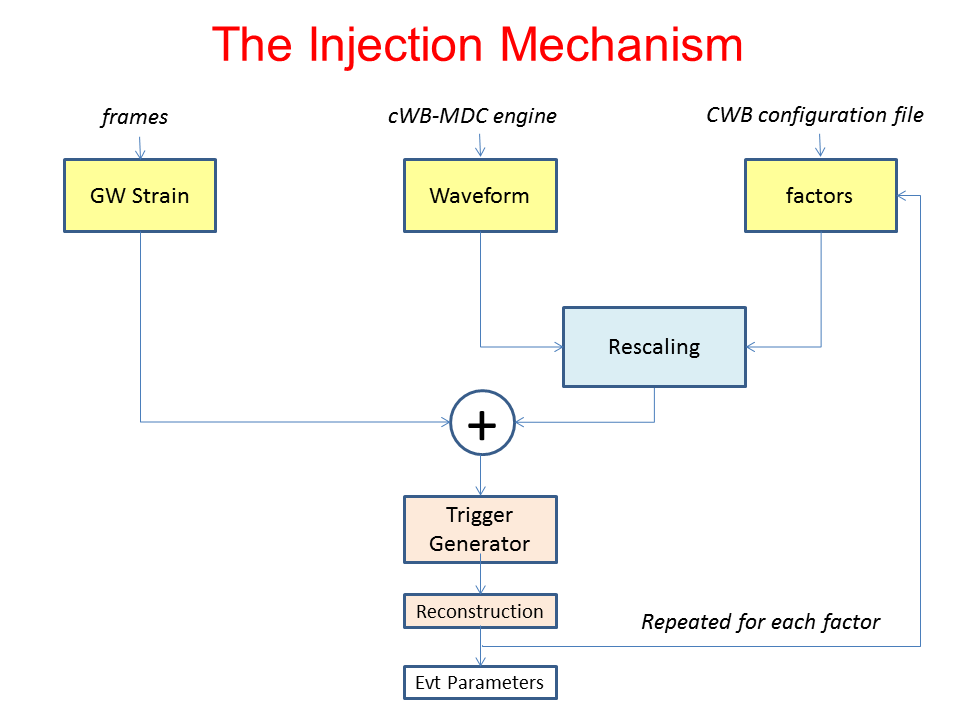
Strain factors¶
The amplitudes of each injected MDC simulated signal can be rescaled by a number of strain factors (to be declared in the user_parameters.C file). This approach increases the available statistic at the price of a limited increase of the computational cost.
The amplitudes of the MDC signals can be rescaled in four different ways, to be selected with the following configuration parameter: simulation (see the description of the simulation parameters). The four methods are summarised in the following list:
- simulation=1 - the factors are used to rescale the hrss of the injected signals. This approach is used to construct detection-efficiency curves, see the Simulation Example
- simulation=2 - the factors are used to rescale the network signal-to-noise ratios of the injected signals.
- simulation=3 - the factors are the time shifts (in seconds) applied to the waveforms
- simulation=4 - the factors are a set of indexes, wich correspond to multiple trials. This approach is used to inject the simulated signals within the desired volume of space.
MDC_Example¶
The mdc class is designed to easily produce mdc data for simulation
See class CWB::mdc ->
Example:
I. Init¶
root[] int nIFO = 3; // number of detectors
root[] TString ifo[3] = {"L1","H1","V1"};
root[] CWB::mdc MDC(nIFO,ifo); // create a mdc object
root[] vector par; // used for MDC parameter definitions
II. Configuration¶
II.1 Set Injection Params¶
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] // define injection parameters
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] MDC.SetInjHrss(2.5e-21); // Set injection HRSS
root[] MDC.SetInjRate(0.0333333); // Set Injection Rate (Hz)
root[] MDC.SetInjJitter(10.0); // Set Time Jitter (sec)
II.2 Add Waveforms¶
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] // Add SinGaussian waveform
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] par.resize(2);
root[] par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=235.;
root[] par[1].name="Q"; par[1].value=8.9;
root[] MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_SG, par);
root[] MDC.Print(); // list defined waveforms
II.3 Set SkyDistribution¶
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] // define sky distribution
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] par.resize(3);
root[] par[0].name="entries";par[0].value=100000; // pool of events
root[] par[1].name="rho_min";par[1].value=1; // min rho // Kpc
root[] par[2].name="rho_max";par[2].value=100; // max rho // Kpc
root[] MDC.SetSkyDistribution(MDC_RANDOM,par,seed);
III. Get Data¶
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] // get data
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] wavearray x;
root[] x.start(0);x.rate(16384);x.size(600*x.rate());
root[] MDC.Get(x,ifo[0]);
IV. Write Frame¶
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] // write frame
root[] // --------------------------------------------------------
root[] TString frDir = "frames";
root[] TString frLabel = "TEST";
root[] size_t gps = 123456789;
root[] size_t length = 1000; // sec
root[] bool log = true;
root[] TString ofName = MDC.WriteFrameFile(frDir, frLabel, gps, length, log);
A Quick Overview¶
This page provides a coincise overview of the options which can be set when generating MDC simulated signals.
- Waveforms
- Built-in Burst-like signals (linearly- or circularly-polarised sine-gaussian, band-limited white noise, linearly-, circularly- or elliptically-polarised ringdown);
- Signals from coalescing binaries (generated via the lalapps_inspinj executable of the LAL library)
- User-defined signals (defined via text files reporting series in the time or frequency domains, at the desired rate)
- Sky Distributions
- Built-in distributions (uniform, based on Galaxy Catalogs or based on the Miyamoto-Nagai modelization of the Milky Way)
- User-defined distributions:
- From file (WaveMDC or BurstMDC log file)
- Fixed Earth/Celestial Position
- Time
- injection rate
- injection time
- fixed
- jittered within a specific time interval
- defined by the user as an input file
- Generation of mdc signals
- On the fly (requires CWB plugins)
- Saving the signal on frame files. Following the procedure used for the BurstMDC and NINJA/LAL simulation studies, this approach generates also a log file with the parameters of the injections.
- Generate frames & log (with condor)
- MDC are saved to disk in frame format (like BurstMDC & NINJA/LAL)
The Injection Params¶
The following injection parameters can be set:
double inj_hrss = 2.5e-21; // source hrss=(h+^2 + hx^2) 10 Kpc
double inj_rate = 0.01; // 1 injection every 100 sec
double inj_jitter = 10.0; // 10 sec jitter
MDC.SetInjHrss(inj_hrss); // Set injection HRSS
MDC.SetInjRate(inj_rate); // Set Injection Rate (Hz)
MDC.SetInjJitter(inj_jitter); // Set Time Jitter (sec)
The Waveforms¶
Builtin waveforms (Burst)
To add a builtin waveform to the MDC object the following instruction must be used : MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_TYPE, par); Ex : TestMDC.C Creates CWB::mdc object and setup of waveforms, sky distribution where MDC_TYPE can be one of the following types : MDC_SG = Linear SinGaussian MDC_SGC = Circular SinGaussian MDC_SGE = Elliptical SinGaussian // created as SGC (ellipticity must be defined by iota) vector<mdcpar> par(2); par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=XXX; // Hz par[1].name="Q"; par[1].value=YYY; Ex : S6A_R4_SIM_BRST_L1H1V1_SGW Scalar GW simulations analysis using On The Fly Burst MDC MDC_RD = Linear RingDown MDC_RDC = Circular RingDown MDC_RDE = Elliptical RingDown // created as RGC (ellipticity must be defined by iota) vector<mdcpar> par(2); par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=XXX; // Hz par[1].name="tau"; par[1].value=YYY; MDC_WNB = White Noise Burst vector<mdcpar> par(3); par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=XXX; // Hz par[1].name="bandwidth"; par[1].value=YYY; // Hz par[2].name="duration"; par[2].value=ZZZ; // sec par[3].name="pseed"; par[3].value=ppp; // seed fo hp component par[4].name="xseed"; par[4].value=xxx; // seed fo hx component par[5].name="mode"; par[5].value=mmm; // 0/1 a/symmetric respect to the central freq Ex : S6A_R4_SIM_BRST_L1H1V1_SGW Scalar GW simulations analysis using On The Fly Burst MDC MDC_GA = Gaussian Burst vector<mdcpar> par(1); par[0].name="duration"; par[0].value=XXX; // sec Ex : S6A_R4_SIM_BRST_L1H1V1_SGW Scalar GW simulations analysis using On The Fly Burst MDC DC_EBBH = Eccentric Binary Black Holes // created as Circular (ellipticity must be defined by iota) // are generated with hrss distance GM/c^2 meters // custom hrss is disabled vector<mdcpar> par(1); par[0].name="file_name"; // ebbh list file name [.lst/.root] // .lst format : one event for each line // -> m1 m2 rp0 e0 (hp,hx are generated 'On The Fly') // .root format : one event for each entry // -> id m1 m2 rp0 e0 hp hx par[1].name="tree cuts"; // optional : used .root file to select tree entries Ex : ADV_SIM_EBBH_L1H1V1 Show how to use the eBBH waveforms with the 2G cwb pipeline Ex : CreateListEBBH.C Macro to create the list of eBBH parameters Ex : DrawEBHH.C This macro use getEBBH & display eBBH hp,hx new Ex : DrawRootEBBH.C Ex : List2RootEBBH.C Convert eBBH file list to a root file which contains the eBBH waveforms Ex : RescaleEBBH.C rescale the strain of eBBH according to the distance of the source
- User defined waveformsUser can define a custom waveform.The following methods are availables :
AddWaveform(TString mdc_name, TString hp_fName); Input: mdc_name - name of mdc hp_fName - name of the input text file which contains hp component NOTE: the input text file is composed by two columns of ascii values (time hp) AddWaveform(TString mdc_name, TString hp_fName, TString hx_fName); Input: mdc_name - name of mdc hp_fName - name of the input text file which contains hp component hx_fName - name of the input text file which contains hx component NOTE: the input text file is composed by two columns of ascii values (time hp/hx) AddWaveform(TString mdc_name, TString hp_fName, double srate); Input: mdc_name - name of mdc hp_fName - name of the input text file which contains hp component srate - sample rate of the input waveform (Hz) NOTE: the input text file s composed by a column of ascii values (hp/hx) at constant sample rate (srate) AddWaveform(TString mdc_name, TString hp_fName, TString hx_fName, double srate); Input: mdc_name - name of mdc hp_fName - name of the input text file which contains hp component hx_fName - name of the input text file which contains hx component srate - sample rate of the input waveform (Hz) NOTE: the input text file s composed by a column of ascii values (hp/hx) at constant sample rate (srate) Ex : LoadWaveforms.C Shows how to load user defined waveforms from files AddWaveform(waveform wf) Input: wf - waveform structure Ex : LoadWaveforms.C Shows how to load user defined waveforms from files
LAL waveforms - (CBC)
SetInspiral(TString inspName, TString inspOptions) Set inspiral mdc parameters Input: inspName - name of inspiral inspOptions - list of options (see lalapps_inspinj options) to dump all the available options do: 'lalapps_inspinj --help' for any details refer to the LAL documentation. There are some special options added only for the mdc class --approximant : is used as alternative to --waveform to force the use of the new XLALSimInspiralChooseWaveformFromSimInspiral --xml "file.xml" : read mdc injection's parameters from xml file --output "file.xml" : write mdc injection's parameters to xml file --dir "tmp dir" : directory used to store temporary xml file, default=/tmp Ex : DrawInspiral.C Shows how to use mdc class to get & draw LAL inpiral waveforms Ex : DrawInspiralFeatures.C Show how to get signal envelop/instant frequency, WignerVille Transform Ex : DrawInspiralUserDet.C Draw Inspiral Waveform with the mdc class (for user defined detectors) Ex : CreateWhitenedInspirals.C Shows how to whitening an inspiral waveform Ex : ADV_SIM_INSPm25m25_L1H1V1 LAL INSPm25m25 with adv detector simu noise and network L1H1V1 Ex : ADV_SIM_INSPm25m25_L1H2H3V1 LAL INSPm25m25 with adv detector simu noise and network L1H2H3V1 Ex : ADV_SIM_NSNS_L1H1V1_2G LAL NSNS with advanced detector simulated noise Ex : ADV_HJLV_SIM_EOBNRv2 LAL EOBNRv2 with advanced detector simulated noise
Builtin waveforms examples :
Add Gaussian (GA) waveform
vector<mdcpar> par(1); par[0].name="duration"; par[0].value=0.004; // define duration MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_GA, par); // add GA4d000 to MDC object
Add Linear Polarized SinGaussian (SG) waveform
vector<mdcpar> par(2); par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=235.; // define frequency par[1].name="Q"; par[1].value=8.9; // define Q MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_SG, par); // add SG235Qd9 to MDC object
Add Circular Polarized SinGaussian (SGC) waveform
vector<mdcpar> par(2); par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=1053.; // define frequency par[1].name="Q"; par[1].value=9; // define Q MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_SGC, par); // add SGC1053Q9 to MDC object
Add White Noise Band (WNB) waveform
vector<mdcpar> par(6); par[0].name="frequency"; par[0].value=250.; // define start frequency (Hz) par[1].name="bandwidth"; par[1].value=100.; // define wideband (Hz) par[2].name="duration"; par[2].value=0.1; // define duration (sec) for(int m=0;m<30;m++) { par[3].name="pseed"; par[3].value=100000+n*100+m; // seed for random noise par[4].name="xseed"; par[4].value=100001+n*100+m; // seed for random noise par[5].name="mode"; par[5].value=1; // 1:freq-simmetric - 2:freq-asymmetric MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_WNB, par); // add WNB_250_100_0d100 to MDC object }
Add eBBH waveform
vector<mdcpar> par(1); par[0].name="macro/eBBH.lst"; MDC.AddWaveform(MDC_EBBH, par); //add eBBH to MDC object where eBBH.lst is (Ex.) : # m1 m2 rp0 e0 0 21.724124 22.576595 13.769443 0.14255266 1 14.041368 16.447480 17.734200 0.19790537 2 16.138471 16.168646 17.070444 0.28757244 3 19.835165 23.344931 14.073969 0.14751020 ...
User defined waveforms examples :
Add User Defined waveform
waveform wf; // waveform structure wavearray<double> x; // temporary buffer used to read waveform TString mdc_name = "SG235Q9"; // waveform name double rate = 16384; // waveform sample rate TString fName = "SG235Q9.txt"; // waveform file name MDC.ReadWaveform(x, fName, rate); // read waveform // build waveform wf.name = mdc_name; wf.type = MDC_USER; wf.hpPath = fName; wf.hp = x; wf.hxPath = ""; wf.hx = wf.hp; wf.hx = 0; // set to 0 the hx component wf.par=""; MDC.AddWaveform(wf); // add waveform
LAL waveforms examples :
Define EOBNRv2 waveform
// --------------------------------- // set inspiral parms // --------------------------------- TString inspOptions=""; inspOptions = "--time-step 60.0 --time-interval 3 "; inspOptions+= "--l-distr random "; inspOptions+= "--gps-start-time 931072130 --gps-end-time 933491330 "; inspOptions+= "--d-distr volume --m-distr totalMassRatio --i-distr uniform "; inspOptions+= "--f-lower 10.000000 "; inspOptions+= "--min-mass1 25.000000 --max-mass1 225.000000 "; inspOptions+= "--min-mass2 25.000000 --max-mass2 225.000000 "; inspOptions+= "--min-mtotal 50.000000 --max-mtotal 250.000000 "; inspOptions+= "--min-mratio 0.25 --max-mratio 1.000000 "; inspOptions+= "--min-distance 1000000.0 --max-distance 1500000.0 "; inspOptions+= "--approximant EOBNRv2pseudoFourPN --disable-spin "; inspOptions+= "--taper-injection start --seed 123456789 "; inspOptions+= "--output inspirals.xml "; // set output xml file // set and write xml file MDC.SetInspiral("EOBNRv2",inspOptions); // set inspiral using xml file (speedup GetInspiral method) TString inspOptions="--xml inspirals.xml"; MDC.SetInspiral("EOBNRv2",inspOptions);
The Sky Distribution¶
Definition of the sky distribution
SetSkyDistribution(MDC_DISTRIBUTION sky_distribution, TString fName, vector<mdcpar> par, int seed, bool add)
Set Sky Distribution
Input: sky_distribution - sky distribution type
fName - input file name
par - input sky distribution parameters
seed - seed for random selection
add - add (def=false) if true the distribution is added to the current one
sky_distribution & par & fName can be one of the following choices :
MDC_RANDOM = random sky distribution (fName not used)
fName can be used to define a custom rho distribution
example : fName="pow(x,2)"
do not use par[n].name="rho_dist";
vector<mdcpar> par(1);
par[0].name="entries"; par[0].value=XXX; // number of random events
par.resize(3);
par[1].name="rho_min"; par[1].value=MIN; // min distance in kPc
par[2].name="rho_max"; par[2].value=MAX; // max distance in kPc
// if(rho_min>0 && rho_max>=rho_min)
// the amplitude is rescaled to 10/rho
// (10 Kpc is the stantard candle distance)
// if rho_min,rho_max are not defined the amplitude is not rescaled
//
par[n].name="rho_dist"; // define the rho distribution
par[n].value=x; // dist is rho^x
// if "rho_dist" is not defined then the distance of events
// is randomly selected from a (rho*rho) distribution
// so the sky distribution is uniform in area
par[m].name="iota"; par[m].value=iota; // ellipticity [0:180] deg
// if<0 || >180 -> random
MDC_EARTH_FIX = earth fixed coordinate
MDC_CELESTIAL_FIX = celestial fixed coordinates
vector<mdcpar> par(2);
par[0].name="theta"; par[0].value=XXX; // degrees
par[1].name="phi"; par[1].value=YYY; // degrees
par.resize(3);
par[2].name="psi"; par[2].value=ZZZ; // degrees
par.resize(4);
par[3].name="rho"; par[3].value=UUU; // kPc
par.resize(5);
par[4].name="gps"; par[4].value=VVV; // sec
par.resize(6);
par[5].name="entries"; par[5].value=TTT; // number of random events
par.resize(7);
par[6].name="iota"; par[6].value=iota; // ellipticity [0:180] deg
// if<0 || >180 -> random
MDC_MNGD = Miyamoto-Nagai Galactic Disk Model (fName,par not used)
www.astro.utu.fi/~cflynn/galdyn/lecture4.html
vector<mdcpar> par(1);
par[0].name="entries"; par[0].value=XXX; // number of random events
par.resize(2);
par[1].name="iota"; par[1].value=iota; // ellipticity [0:180] deg
// if<0 || >180 -> random
MDC_GWGC = Gravitation Wave Galaxy Catalog (par not used)
fName = path name of galaxy catalog
vector<mdcpar> par(1);
par[0].name="distance_thr"; par[0].value=XXX; // distance max (Kpc)
par.resize(2);
par[1].name="iota"; par[1].value=iota; // ellipticity [0:180] deg
// if<0 || >180 -> random
MDC_LOGFILE = mdc log file
fName = path name of mdc log file
MDC_CUSTOM = user define distribution
fName = path name of user file
file format : gps name theta phi psi rho iota hrss ID id
theta = [0:180] deg : phi = [0:360] deg
psi = [0:180] deg : iota = [0:180] deg
ID/id are the major/minor id waveform numbers
if ID=-1 then 'name' is used, if id=1 then id is selected randomly
Note1: the angle iota is the inclination of the system which originates
the burst with respect to the line of sight
iota = 0 : the line of sight is perpendicular to the orbit plane
iota = 90 : the line of sight has 0 deg inclination angle respect to the orbit plane
the h+ ellipticity factor is : (1+cos[iota]*cos[iota])/2
the hx ellipticity factor is : cos[iota]
Note2: rho defines the distance of the source in Kpc
if rho=0 then the hrss is the one defined with SetInjHrss (default)
if rho>0 then the hrss is rescaled by a factor 10/rho;
the hrss defined with SetInjHrss is the hrss at 10Kpc
Examples :
Random Distribution : rho,theta,phi,psi are randomly distributed
int seed = 0; // random distribution seed vector<mdcpar> par(3); par[0].name="entries";par[0].value=100000; // number of generated random pool events par[1].name="rho_min";par[1].value=1; // min rho (Kpc) par[2].name="rho_max";par[2].value=100; // max rho (Kpc) MDC.SetSkyDistribution(MDC_RANDOM,par,seed);
Fixed earth source direction, fixed psi,gps
vector<mdcpar> par(4); par[0].name="theta"; par[0].value=30; // fixed theta [-90:90] par[1].name="phi"; par[1].value=60; // fixed phi [0:360] par[2].name="psi"; par[2].value=0; // fixed psi [0:180] par[3].name="gps"; par[3].value=968650050; // fixed GPS MDC.SetSkyDistribution(MDC_EARTH_FIX,par);
Fixed celestial source direction
float DEC = -27.687000274658; float RA = 3.4909999370575; float seed = 0; vector<mdcpar> par(3); par[0].name="theta"; par[0].value=DEC; par[1].name="phi"; par[1].value=RA; par[2].name="entries"; par[2].value=1000; // generates a pool of 1000 events with random psi MDC.SetSkyDistribution(MDC_CELESTIAL_FIX,par,seed);
Gravitational Wave Galaxy Catalog distribution
vector<mdcpar> par(1); par[0].name="distance_thr"; par[0].value=100; // select max distance = 100 Mpc MDC.SetSkyDistribution(MDC_GWGC,"GWGCCatalog_Rev1d8.txt",par); // load GWGC catalog Ex : TestDrawDistributions.C Draw Sky Distributions Ex : ConvertGWGC.C convert GWGCCatalog_Rev1d8.txt format to SetSkyDistribution format Ex : ADV_SIM_BRST_LF_GWGC_L1H1V1 Simulation with a "On the Fly" GWGC distribution up to 50Mpc Ex : ADV_SIM_BRST_LF_GWGC_L1H1_1G Simulation with a "On the Fly" GWGC distribution and L1H1 network There is a local copy in $CWB_GWAT/data/GWGCCatalog_Rev1d8.txt The catalog has been downloaded from: https://www.lsc-group.phys.uwm.edu/cgi-bin/pcvs/viewcvs.cgi/bursts/collabs/DO_proposal/ \ gwgc/GWGCCatalog.txt?cvsroot=lscdocs The GWGC documentation is here : https://www.lsc-group.phys.uwm.edu/cgi-bin/pcvs/viewcvs.cgi/bursts/collabs/DO_proposal/ \ gwgc/GWGCReadme.pdf?cvsroot=lscdocs
Miyamoto-Nagai Galactic Disk Model
vector<mdcpar> par(1); par[0].name="entries";par[0].value=100000; // number of random entries MDC.SetSkyDistribution(MDC_MNGD,par); Ex : ADV_SIM_SGQ9_L1H1V1_2G // see macro/CreateFramesMDC.C Ex : ADV_SIM_SGQ9_L1H1V1_SKYMASK // see macro/CreateFramesMDC.C Ex : ADV_SIM_SGQ9_L1H1V1_TST // see macro/CreateFramesMDC.C Ex : ADV_SIM_SGQ9_L1Y2Y3V1_TST // see macro/CreateFramesMDC.C