Handling PSDs¶
Reading / Saving a PSD from a file¶
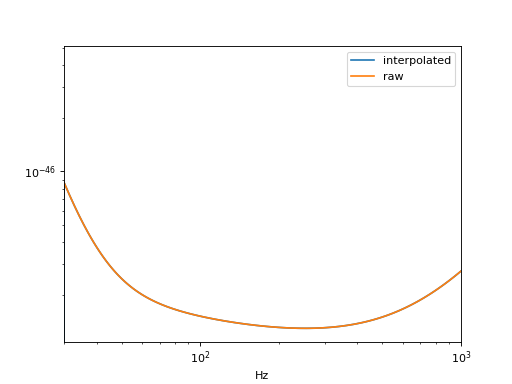
If you have a PSD in a two column, space separated, (frequency strain), you can load this into PyCBC.
import pycbc.psd
import pycbc.types
import pylab
filename = 'example_psd.txt'
# The PSD will be interpolated to the requested frequency spacing
delta_f = 1.0 / 4
length = int(1024 / delta_f)
low_frequency_cutoff = 30.0
psd = pycbc.psd.from_txt(filename, length, delta_f,
low_frequency_cutoff, is_asd_file=False)
pylab.loglog(psd.sample_frequencies, psd, label='interpolated')
# The PSD will be read in without modification
psd = pycbc.types.load_frequencyseries('./example_psd.txt')
pylab.loglog(psd.sample_frequencies, psd, label='raw')
pylab.xlim(xmin=30, xmax=1000)
pylab.legend()
pylab.xlabel('Hz')
pylab.show()
# Save a psd to file, several formats are supported (.txt, .hdf, .npy)
psd.save('tmp_psd.txt')
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Generating an Analytic PSD from lalsimulation¶
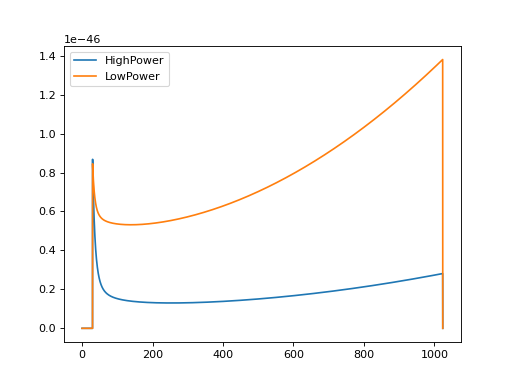
A certain number of PSDs are built into lalsimulation, which you’ll be able to access through PyCBC. Below we show how to see which ones are available, and demonstrate how to generate one.
import pycbc.psd
import pylab
# List the available analytic psds
print(pycbc.psd.get_lalsim_psd_list())
delta_f = 1.0 / 4
flen = int(1024 / delta_f)
low_frequency_cutoff = 30.0
# One can either call the psd generator by name
p1 = pycbc.psd.aLIGOZeroDetHighPower(flen, delta_f, low_frequency_cutoff)
# or by using the name as a string.
p2 = pycbc.psd.from_string('aLIGOZeroDetLowPower', flen, delta_f, low_frequency_cutoff)
pylab.plot(p1.sample_frequencies, p1, label='HighPower')
pylab.plot(p2.sample_frequencies, p2, label='LowPower')
pylab.legend()
pylab.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
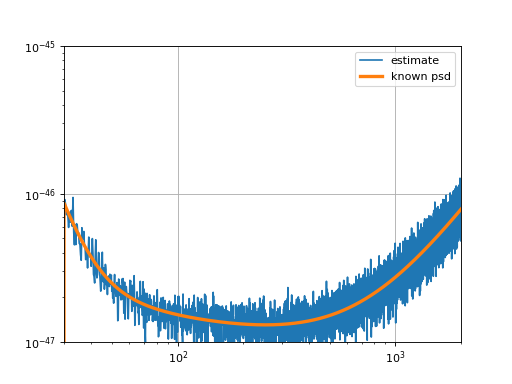
Estimating the PSD of a time series¶
import pycbc.noise
import pycbc.psd
import pylab
# generate some colored gaussian noise
flow = 30.0
delta_f = 1.0 / 16
flen = int(2048 / delta_f) + 1
psd = pycbc.psd.aLIGOZeroDetHighPower(flen, delta_f, flow)
### Generate 128 seconds of noise at 4096 Hz
delta_t = 1.0 / 4096
tsamples = int(128 / delta_t)
ts = pycbc.noise.noise_from_psd(tsamples, delta_t, psd, seed=127)
# Estimate the PSD
## We'll choose 4 seconds PSD samples that are overlapped 50 %
seg_len = int(4 / delta_t)
seg_stride = int(seg_len / 2)
estimated_psd = pycbc.psd.welch(ts,
seg_len=seg_len,
seg_stride=seg_stride)
pylab.loglog(estimated_psd.sample_frequencies, estimated_psd, label='estimate')
pylab.loglog(psd.sample_frequencies, psd, linewidth=3, label='known psd')
pylab.xlim(xmin=flow, xmax=2000)
pylab.ylim(1e-47, 1e-45)
pylab.legend()
pylab.grid()
pylab.show()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)